Food is culture. This is especially true in a food-obsessed country like Japan where the national cuisine uniquely reflects the natural environment, regional diversity and underlying value system of this resilient country. Japan is the second largest e commerce market in the Asia-Pacific region. Because of the high number of households with Internet access, more Japanese consumers are switching to online shopping. However, the use of e commerce for fresh food is very limited in Japan. This provides a significant opportunity for the meat substitute manufacturers to promote and sell their products in Japan.
Japanese consumers are sophisticated, highly conscious of food quality and safety, and willing to pay for attributes they believe define a high-quality, safe product. A recent series of domestic and international food safety crises have elevated the importance of meat safety among Japanese consumers. The Japanese government and food industry are implementing new policies and systems intended to assure consumers that the food supply is safe and wholesome. Protein-rich, low-calorie soy products have long been a major player in Japanese diets. Tofu and natto are commonly found at all supermarkets and convenience stores in Japan. Thus, the trend for meat substitute is expected to flourish in Japan over the forecast period and many small and large players can untap this opportunity to expand and generate high revenue.
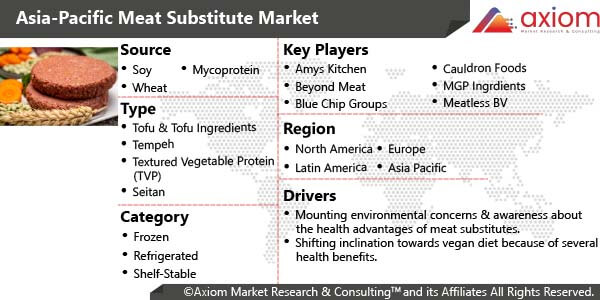
Asia-Pacific Meat Substitute Market Outlook
The major factors driving the Asia-Pacific Meat Substitute market are rising environment concern around the world, reduction in meat consumption, growing health concerns, changing dietary pattern, increased preference for vegetarian and vegan foods and limited meat production. However, health concerns surrounding meat alternatives and high cost of meat substitutes are some of the restrains faced by the market.
Asia-Pacific Meat Substitute Market Segmental Overview
The Asia-Pacific Meat Substitute market is segmented based on type, source, category, distribution channel and country.
Asia-Pacific Meat Substitute Market by Type
The Asia-Pacific Meat Substitute market by service is segmented into tofu & tofu ingredients, tempeh, textured vegetable protein, seitan, quorn and others. The tofu & tofu ingredients segment accounted for the second largest share of the meat substitutes market in 2018, followed by tempeh segment. Meat substitutes such as tempeh and tofu are rich in proteins and minerals, since they are derived from soy; moreover, they have become a popular meat alternative among vegetarians and vegan consumers for their health benefits. Tofu-based products (tofu skin, okara, and tofurkey) are expected to emerge as developing segment over the forecast period, but its growth rate is likely to be lower as compared to another segment.
APAC is estimated to be the major revenue contributor to the tofu market as a meat substitute throughout the forecast period. Soy-based foods are easily digestible and have a high amount of protein and high nutritional values. This will increase the preference of consumers in this region towards soy-based foods such as tofu. Additionally, the increasing demand for nutritional diet and the rising disposable income will also play a significant role in the growth of the market in APAC. Countries such as China, Japan, South Korea, Vietnam, the Philippines, Thailand, and Indonesia will be the major contributors to the tofu market in this region.
Asia-Pacific Meat Substitute Market by Source
Meat substitutes are obtained from various sources such as soy, wheat, mycoprotein and others. Other sources of meat substitute include mushrooms, lentils, beans, etc. Among the various source, soy-based meat substitute products accounted for the largest market share, followed by mycoprotein, in 2018. This is because soy protein is a cost-effective and reliable substitute for meat and has the highest amount of protein as compared to other meat substitutes. Soy-based meat substitutes can be produced to mimic the organoleptic characteristics of meat products. Soy burgers, soy turkey, soy bacon, soy chicken, and soy hot dogs are a few popular soy-based food products. Moreover, soy is the most common source of meat substitutes in Asia-Pacific. Increasing demand for tofu from food service and beverage manufacturers depicts its popularity. Soy-based products are rich in amino acids, vitamins, fibers, omega-3, and flavones, in addition to being cholesterol-free and low in saturated fat. Soya meat is extremely rich in protein, with a protein content over 50%. Owing to these advantages, soy-based meat substitutes are anticipated to increase their market presence. Soy meat alternatives are closer to the taste and texture of meat, than in the past, because of newer technology. These developments have led to increased demand of these substitutes from the consumers.
Asia-Pacific Meat Substitute Market by Category
The various categories by which the Asia-Pacific Meat Substitute Market is sectioned includes frozen, refrigerated and shelf-stable. Frozen function segment accounted for the largest market share in 2018. Refrigerated meat substitutes were the second largest market after frozen meat substitutes. Generations view protein differently, with older generations more concerned about the health benefits of protein and younger generations caring about exercise recovery and feeling full.
Asia-Pacific Meat Substitute Market by Distribution Channel
The Asia-Pacific Meat Substitute Market by distribution channel is segmented into direct and indirect. The indirect distribution channel was the major contributor to the Asia-Pacific meat substitute market based on value. Due to various advantages of direct distribution channel such as low cost, limited coverage, time consuming; it was overshadowed by the indirect distribution channel.
Asia-Pacific Meat Substitute Market by Country
The various countries studied in this report include China, Japan, India, and Rest of the Asia Pacific. The Chinese government has issued new dietary guidelines recommended by the country’s Health Ministry, which aim to reduce the country’s meat consumption in half by 2030. China consumes around 30 percent of the world’s meat, including half of its pork, even though average per capita meat consumption is half that of the average American or Australian. The guidelines recommend eating around 40-75 grams of meat per day, closer to recommendations made by the UK Department of Health.
Also, vegetarianism is gaining popularity slowly in Japan, driven by health, environmental, and animal welfare concerns. Although the more conscious display a general willingness to reduce meat consumption, many consumers will find it hard to give up the taste and texture associated with meat. This provides opportunities to develop and expand meat alternative products, which can satisfy the craving for meat while providing the benefit of plant-based foods to a growing consumer group.
Asia-Pacific Meat Substitute Market-Key Players
The major players involved in this market are Danisco (DuPont), Amys Kitchen, Cargill, Cauldron Foods, MGP Ingredients, Schouten, Morningstar Farms, Quorn Foods, Sonic Biochem, Vbites Foods and ADM among others.